The cost of sales for a software company covers direct expenses such as server hosting, third-party software fees, and wages for development and support teams. It’s essential for managing profitability, pricing, and operational efficiency.
“The cost of sales for a software company refers to the direct expenses related to delivering software products or services, such as server costs and third-party software.”
In this article, We will discuss “What Is Cost Of Sales For A Software Company”
What Is the Cost of Sales for a Software Company?
In the world of software businesses, particularly those offering Software as a Service (SaaS) or subscription-based models, understanding and accurately calculating the Cost of Sales (also referred to as Cost of Goods Sold or COGS) is crucial for financial planning. It helps in evaluating profitability, pricing strategies, and overall financial health.
The cost of sales reflects all the direct expenses associated with delivering a software product or service to your customers. Let’s dive deeper into what this entails, why it’s important, and how to calculate it for your software business.
1. What Does the Cost of Sales Include for a Software Company?
For software companies, the cost of sales typically includes the following:
a. Server and Hosting Costs:
Software products, especially cloud-based applications, rely heavily on servers and cloud infrastructure to function. These are often hosted on platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) , Microsoft Azure , or Google Cloud .
The costs of maintaining these servers, handling data traffic, and scaling the infrastructure to accommodate user growth directly impact the cost of delivering the software to customers.
Also Read: How To Disable Keys On Womier Software – How to Use It!
b. Third-Party Software and API Fees:
Most software products integrate third-party tools or services through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). For example, if a SaaS product uses a payment processor like Stripe or a communication tool like Twilio , the associated fees become part of the cost of sales.
These third-party tools are integral to delivering the service, making their expenses a direct cost.
c. Salaries for Product Development and Support Teams:
The salaries of employees who are directly responsible for creating and delivering the software also fall under the cost of sales. This includes developers, software engineers, and support teams .
For example, the cost of maintaining a support team that handles customer inquiries, bugs, or technical issues is essential for the operation of the product and directly influences the overall cost of sales.
d. Data Storage and Security Costs:
Storing user data securely is a legal and operational necessity for many software companies. Costs associated with databases, security systems, encryption, and compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA are direct costs that affect the overall delivery of the software.
e. Licensing Fees for Software Components:
If the software uses any licensed technology or external components (such as open-source licenses with commercial terms), these fees are part of the cost of sales. For instance, if your software incorporates licensed video streaming technology or analytics platforms, the associated costs would be included.
2. What Doesn’t Count as Cost of Sales?
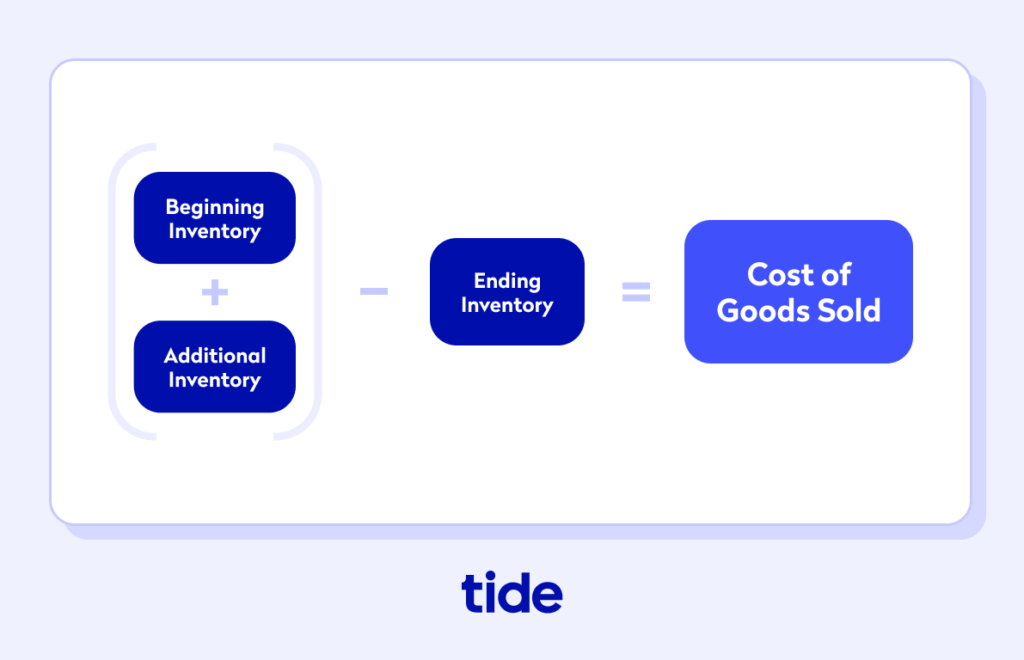
It’s essential to differentiate between cost of sales and operating expenses to maintain financial clarity. The following expenses are not included in the cost of sales for software companies:
a. Sales and Marketing Costs:
Although marketing and sales efforts are critical for attracting and retaining customers, they don’t directly contribute to the production or delivery of the product. Therefore, costs associated with advertising, promotions, and salaries of salespeople fall under operating expenses.
b. General Administrative Costs:
Administrative expenses such as office rent, utilities, executive salaries, and other overhead costs are not included in the cost of sales. These fall under the broader category of General and Administrative (G&A) expenses.
Also Read: How To Delete An Epomaker Software Account – An Easy Guide!
c. Research and Development (R&D) Costs:
While product development is part of the cost of sales, the broader R&D efforts to explore new features or develop new products are typically considered operating expenses. This includes time spent on innovation, product enhancements, or developing completely new product lines.
3. How Is Cost of Sales Different from Operating Expenses?
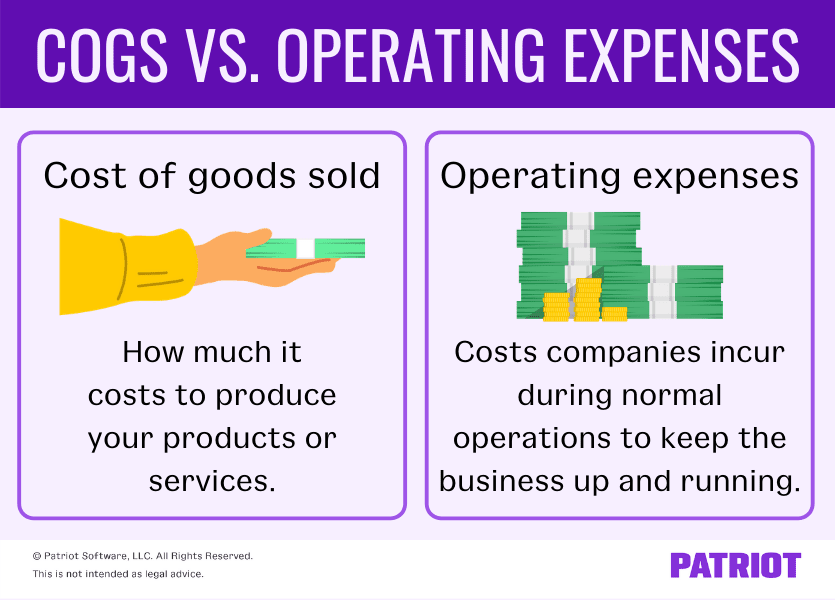
Operating expenses (Op Ex) cover all business expenses that aren’t directly tied to producing the product or service. These include overheads like marketing, administrative salaries, office rent, and other operational costs. In contrast, cost of sales focuses strictly on the direct expenses involved in delivering your software.
For example, the salary of a software engineer working on feature development for your SaaS product would be part of the cost of sales. But the salary of a marketing manager, even though they are crucial to selling the software, would be categorized as an operating expense.
Understanding this distinction helps businesses accurately track their financial performance, as operating expenses are deducted after calculating gross profit , while cost of sales directly affects gross margin .
4. Why Is It Important to Track the Cost of Sales?
Accurately tracking the cost of sales is vital for several reasons:
a. Determining Profit Margins:
By understanding the direct costs of delivering your software product, you can accurately calculate your gross margin, the revenue generated minus the cost of sales. This figure is critical to understanding how profitable your software is on a per-unit basis before considering broader operational costs.
b. Pricing Strategy:
Also Read: Software Updates Error Id 3104046 – A Step-by-Step Guide!
Understanding the cost of sales is essential for setting the right price for your software. If you underestimate the cost, you could price your product too low and harm your profitability. On the other hand, knowing your costs allows you to price your product competitively while still ensuring a healthy margin.
c. Cost Management and Optimization:
Tracking the cost of sales over time helps identify areas where spending can be optimized. For example, if server costs are increasing rapidly due to user growth, a company might look for more efficient cloud solutions or negotiate better terms with their hosting providers.
5. How to Calculate the Cost of Sales for a Software Company?
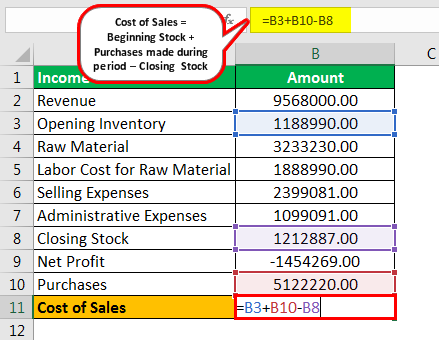
The calculation of cost of sales for a software company is straightforward once you have categorized your direct costs. The formula looks like this:
\[
\text{Cost of Sales} = \text{Direct Production Costs} + \text{Labor Costs} + \text{Third-Party Service Costs}
\]
Here’s how it breaks down:
- Direct Production Costs : This includes costs related to servers, data storage, and third-party services, which are essential for running the software infrastructure.
- Labor Costs : Wages for employees involved in development, deployment, and customer support, directly contributing to the creation and maintenance of the software product.
- Third-Party Service Costs : Fees paid to external services or API providers that are part of the product, ensuring seamless integration and enhanced functionality.
Each company’s calculation may vary based on its specific operational structure, but the focus is always on capturing the direct costs involved in delivering the software product or service to customers.
6. Examples of Cost of Sales for Different Types of Software Companies:
a. SaaS Companies:
For SaaS companies, the cost of sales would include server hosting, customer support staff, third-party software integrations, and any direct labor costs related to product delivery. A SaaS company delivering an HR management tool, for example, would account for the servers running the platform, API costs for payment processors, and the support team handling customer inquiries.
Also Read: What Programs does Glarysoft Software Update Pro 6 Look For – Complete Guide!
b. Custom Software Development Firms:
For firms developing custom software solutions, the cost of sales primarily revolves around labor. The time spent by developers and designers on client projects would make up the bulk of the cost of sales. Other direct costs might include software licenses or tools needed to complete the project.
c. Mobile App Developers:
In this case, cost of sales might include app store fees (such as Apple’s App Store or Google Play), the cost of cloud storage, and the salaries of developers who build and maintain the apps. For instance, an app with video streaming capabilities may incur high data storage and bandwidth costs, which would contribute to the cost of sales.
FAQ’s
1. What is the cost of sales for a software company?
The cost of sales includes all direct expenses needed to deliver a software product or service, such as server costs, third-party software fees, and developer wages.
2. What expenses are included in the cost of sales for a software business?
It typically includes server hosting, third-party API costs, direct labor (developers, support), and data storage/security expenses.
3. Are salaries included in the cost of sales for software companies?
Yes, but only for employees directly involved in delivering the product, like developers and support staff.
4. How is the cost of sales different from operating expenses?
Cost of sales covers direct costs to deliver the software, while operating expenses include indirect costs like marketing and administration.
5. Why is it important to track cost of sales in a software company?
Tracking cost of sales helps assess profitability, set accurate pricing, and manage direct costs effectively.
Conclusion
The cost of sales for a software company represents the direct expenses involved in delivering software products or services to customers. It includes costs such as server hosting, third-party tools, and developer salaries, but excludes operating costs like marketing and administration. Understanding and tracking these costs is essential for pricing, profitability, and financial efficiency.



